Surface-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry (SALDI-MS)
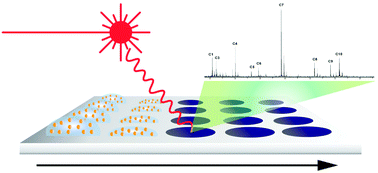
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry has been at the forefront of surface-based mass spectrometric techniques. While amenable to high-throughput analyses and useful for profiling global biological activities, the necessary presence of a UV-absorbing matrix limits effectiveness for discerning analyte signals in the low m/z region (<500 Da). To circumvent this issue, the field of surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (SALDI-MS) has undergone rigorous development and is gaining considerable attention for low molecular weight analytes. SALDI-MS utilizes the properties of the underlying material, rather than a matrix diluent for effective UV absorption and heat transfer towards ionization. As no organic matrix is now present, there is little to no interfering peaks in the low mass region, rendering these materials highly effective for low molecular weight samples (e.g. clinical drugs, carbohydrates, single nucleotides/amino acids). We have developed a number of SALDI active substrates based on nanoglassified gold thin films and nanoparticles. These have been effectively applied toward a range of biomolecules and in microarray formats. We currently have access to a Voyager DE-STR MALDI-TOF mass spectrometer, as well as a MALDI-TOF/TOF 5800 from AB Sciex.
Surface Plasmon Resonance Coupled to Matrix-assisted Laser Desorption Ionization (SPR-MALDI)
SPR-MALDI combines the ability of SPR to stably and quantitatively monitor surface binding events with MALDI-MS's ability to easily qualitatively identify the species involved in those surface binding events. Our custom designed imaging arrays allow facile movement from one analysis type to the other. Using the multifunctional array alone enables SPR imaging detection of biological targets at clinically relevant levels, while characteristic masses (or a digested peptide fingerprint) are identified in the MALDI-MS spectra of the surface after capture, giving unambiguous identification of the target. This hybrid methodology allows the sensitivity and fingerprinting utility of mass spec to be used on a surface where the desired biomarker is sensed in a biologically relevant context and may offer a new technical avenue for bioanalysis in complex media.
Self-Assembled Monolayer Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry (SAMDI-MS)
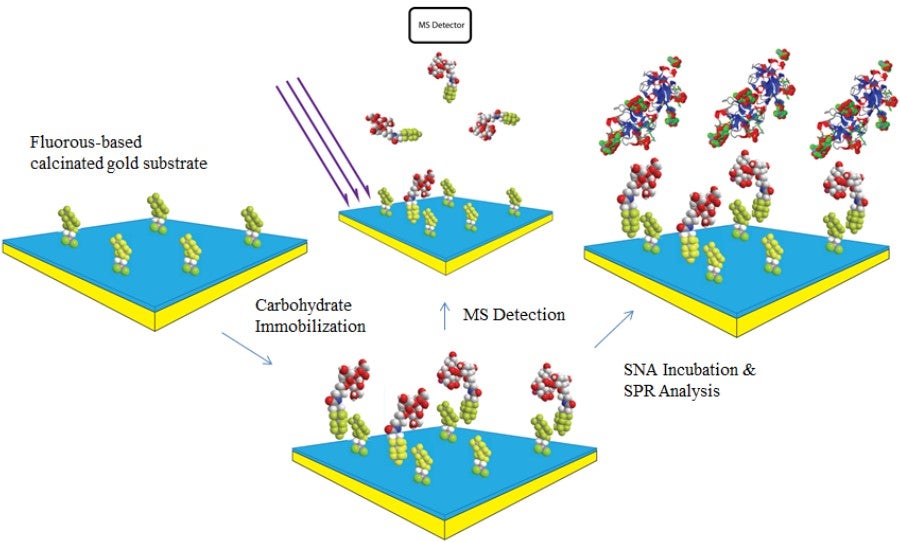
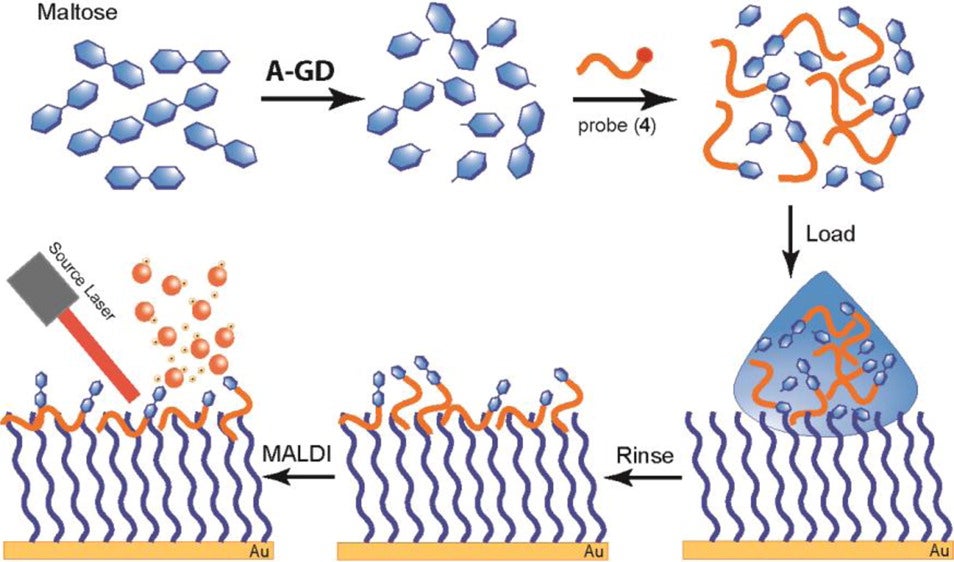
SAMDI-MS is a useful tool for specific analyte capture and on-chip purification from contaminants. Self-assembled monolayers may be created and further functionalized using a variety of surface chemistries on gold. From this point, the biomolecule of interest may be captured directly on-chip, or with a recognition probe in solution that will be specifically captured after an incubation step. Crude samples perform outstandingly on these surfaces, as washing with water or solvent may be carried out before mass spectrometric analysis, leaving only the analyte of interest. We have primarily utilized hydrophobic interactions for both direct and capture probe based purification on C18 and perfluorinated gold surfaces.